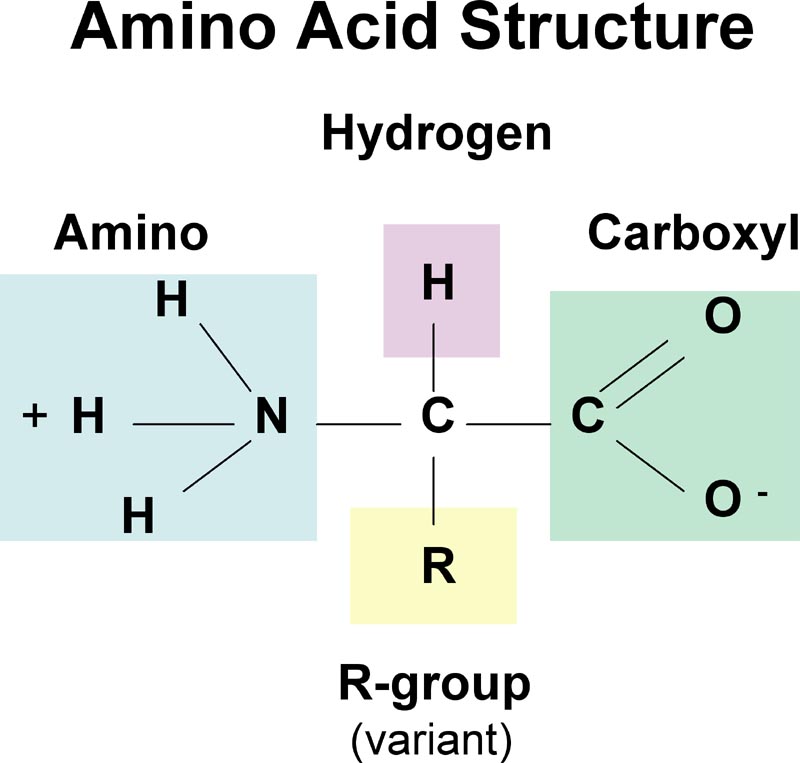
Amino acids are organic compounds that combine to form proteins. Amino acids and proteins are the building blocks of life.
When proteins are digested or broken down, amino acids are left. The human body needs a number of amino acids to:
Break down food
Grow
Repair body tissue
Perform many other body functions
Amino acids are classified into three groups:
- Essential amino acids
- Nonessential amino acids
- Conditional amino acids
Essential amino acids
Essential amino acids cannot be made by the body. As a result, they must come from food.
The nine essential amino acids are: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine.
Nonessential amino acids
"Nonessential" means that our bodies produce an amino acid, even if we don't get it from the food we eat.
They include: alanine, asparagine, aspartic acid, and glutamic acid.
Conditional amino acids
Conditional amino acids are usually not essential, except in times of illness and stress.
They include: arginine, cysteine, glutamine, tyrosine, glycine, ornithine, proline, and serine.
You do not need to eat essential and nonessential amino acids at every meal, but getting a balance of them over the whole day is important.
The twenty amino acids (that make up proteins) each have assigned to them a three-letter code.
alanine – ala –
arginine – arg –
asparagine – asn –
aspartic acid – asp –
cysteine – cys –
glutamine – gln –
glutamic acid – glu –
glycine – gly –
histidine – his –
isoleucine – ile –
leucine – leu –
lysine – lys –
methionine – met –
phenylalanine – phe –
proline – pro –
serine – ser –
threonine – thr –
tryptophan – trp –
tyrosine – tyr –
valine – val –
Sometimes it is not possible two differentiate two closely related amino acids, therefore we have the special cases:
asparagine/aspartic acid – asx –
glutamine/glutamic acid – glx –
Here is list where amino acids are grouped according to the characteristics of the side chains:
Aliphatic – alanine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, proline, valine
Aromatic – phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine
Acidic – aspartic acid, glutamic acid
Basic – arginine, histidine, lysine
Hydroxylic – serine, threonine
Sulphur-containing – cysteine, methionine
Amidic (containing amide group) – asparagine, glutamine