Kinds of teeth
Human beings grow two sets of teeth: (1) deciduous teeth and (2) permanent teeth.
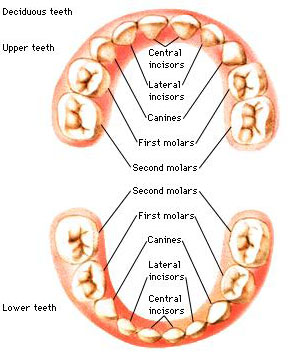
Deciduous
Deciduous teeth are also called baby teeth, milk teeth, or primary teeth.
There are 20 deciduous teeth, 10 of them in each jaw. They consist of three kinds of teeth: (1) incisors, (2) canines, and (3) molars. Each jaw has 4 incisors, 2 canines, and 4 molars. The incisors and canines are used to bite into food, and the molars are used to grind food.
Permanent teeth
There are 32 permanent teeth, 16 in each jaw. They are larger than the deciduous teeth and consist of four kinds of teeth. The four kinds are (1) incisors, (2) canines, (3) premolars, and (4) molars. Each jaw has 4 incisors, 2 canines, 4 premolars, and 6 molars.
Molars, like premolars, are used to grind food. They are shaped much like premolars but are larger. The various molars normally have three to five cusps and two or three roots.
Malocclusion
is the failure of the teeth in the upper and lower jaws to meet properly when a person bites. Normally, the upper front teeth should slightly overlap the lower front teeth. There are three main types of malocclusions, overbite, underbite, and crowding. In overbite, the upper front teeth stick out too far over the lower front teeth. This defect is commonly called buck teeth. In underbite, the lower front teeth extend in front of the upper ones. Many people have the correct occlusion (bite), but their teeth are crowded. Crowding is the most common malocclusion.
Disease
There are three main kinds of periodontal diseases. They are (1) gingivitis, (2) periodontitis, and (3) Vincent's infection.
Gingivitis
is an inflammation of the gingivae (gums). The gingivae become red and swollen and bleed easily when brushed or prodded. Dentists treat gingivitis by cleaning the teeth and gums to remove plaque and calculus. They also instruct patients on how to brush and floss the teeth and on how to massage the gums. If gingivitis is not treated, it can lead to periodontitis.
Periodontitis
also called pyorrhea, is a severe infection of the gingivae, alveolus, and other tissues that support the teeth. The infection gradually destroys the bony walls of the sockets, and the teeth become loose. Periodontitis is difficult to cure, but it can be effectively controlled. Treatment involves surgical or nonsurgical removal of the damaged tissues and repair of the remaining healthy tissues. Some dentists use the heat of a beam from a laser to remove infected tissue. The laser process may quicken healing because it does little damage to the surrounding healthy area. Sometimes, loose teeth can be splinted (attached) to nearby teeth that are still firm. But in many cases, the loose teeth must be removed and replaced by artificial ones.
Trench mouth
Vincent's infection, also called trench mouth, is a painful infection of the gingivae. The gums become red and swollen and bleed easily. The mouth has an extremely bad odor, and the victim may develop a fever. To treat Vincent's infection, a dentist cleans the teeth and gums thoroughly and instructs the patient on mouth care. In most cases, the dentist also prescribes antibiotics to combat the infection.
Some animal teeth
Animal teeth vary in size and shape. Most mammals have heterodont teeth, which consist of two or more types: (1) incisors and (2) canines for biting and tearing food, and (3) molars for crushing it. Most reptiles and many fish have homodont teeth, a single type that generally is used to catch prey.