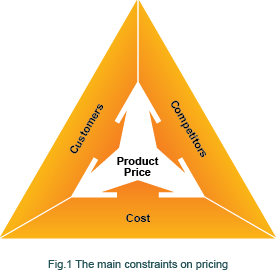
This article gives you guidelines on how to price your products and the typical process used in most companies. At a basic level the main constraints on pricing are the costs associated with your offer, customers’ willingness to pay and your competition (see Fig.1). Product costs set a lower limit below which prices are not viable in the long term. The upper limit is a combination of affordability for your target customers, how they perceive the value of your product and how it compares to the alternatives eg. your competition.
Choosing a pricing strategy
There are three basic pricing strategies. Marketing skimming is setting your pricing high relative to major competitors and is often used if the pricing objective is to maximise profitability. Market penetration is setting your pricing low relative to major competitors and is often used to maximise market share. Finally competitor matching is setting your pricing at a similar level to the competition and is often used to maximise customer retention.