Logic (Deduction and Induction) is one of the three roads from the Trivium.
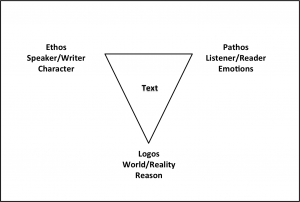
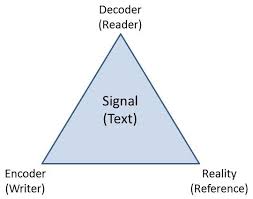
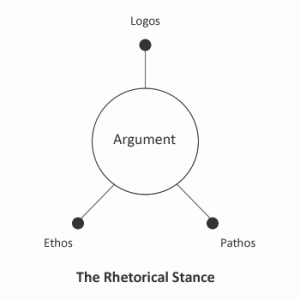
The Subject of Logic: “Syllogisms”
All Aristotle’s logic revolves around one notion: the deduction (sullogismos). A thorough explanation of what a deduction is, and what they are composed of, will necessarily lead us through the whole of his theory. What, then, is a deduction? Aristotle says:
A deduction is speech (logos) in which, certain things having been supposed, something different from those supposed results of necessity because of their being so. (Prior Analytics I.2, 24b18-20)
Each of the “things supposed” is a premise (protasis) of the argument, and what “results of necessity” is the conclusion (sumperasma).

The core of this definition is the notion of “resulting of necessity” (ex anankês sumbainein). This corresponds to a modern notion of logical consequence: X results of necessity from Y and Z if it would be impossible for X to be false when Y and Z are true. We could therefore take this to be a general definition of “valid argument”.
When arguing with someone in an attempt to get at an answer or an explanation, you may come across a person who makes logical fallacies. Such discussions may prove futile. You might try asking for evidence and independent confirmation or provide other hypotheses that give a better or simpler explanation. If this fails, try to pinpoint the problem of your arguer’s position. You might spot the problem of logic that prevents further exploration and attempt to inform your arguer about his fallacy. The following briefly describes some of the most common fallacies:
ad hominem: Latin for “to the man.” An arguer who uses ad hominems attacks the person instead of the argument. Whenever an arguer cannot defend his position with evidence, facts or reason, he or she may resort to attacking an opponent either through: labeling, straw man arguments, name calling, offensive remarks and anger.
appeal to ignorance (argumentum ex silentio) appealing to ignorance as evidence for something. (e.g., We have no evidence that God doesn’t exist, therefore, he must exist. Or: Because we have no knowledge of alien visitors, that means they do not exist). Ignorance about something says nothing about its existence or non-existence.
argument from omniscience: (e.g., All people believe in something. Everyone knows that.) An arguer would need omniscience to know about everyone’s beliefs or disbeliefs or about their knowledge. Beware of words like “all,” “everyone,” “everything,” “absolute.”
appeal to faith: (e.g., if you have no faith, you cannot learn) if the arguer relies on faith as the bases of his argument, then you can gain little from further discussion. Faith, by definition, relies on a belief that does not rest on logic or evidence. Faith depends on irrational thought and produces intransigence.
appeal to tradition (similar to the bandwagon fallacy): (e.g., astrology, religion, slavery) just because people practice a tradition, says nothing about its viability.
argument from authority (argumentum ad verecundiam): using the words of an “expert” or authority as the bases of the argument instead of using the logic or evidence that supports an argument. (e.g., Professor so-and-so believes in creation-science.) Simply because an authority makes a claim does not necessarily mean he got it right. If an arguer presents the testimony from an expert, look to see if it accompanies reason and sources of evidence behind it.
Appeal to consequences (argumentum ad consequentiam): an argument that concludes a premise (usually a belief) as either true or false based on whether the premise leads to desirable or undesirable consequences. Example: some religious people believe that knowledge of evolution leads to immorality, therefore evolution proves false. Even if teaching evolution did lead to immorality, it would not imply a falsehood of evolution.
argument from adverse consequences: (e.g., We should judge the accused as guilty, otherwise others will commit similar crimes) Just because a repugnant crime or act occurred, does not necessarily mean that a defendant committed the crime or that we should judge him guilty. (Or: disasters occur because God punishes non-believers; therefore, we should all believe in God) Just because calamities or tragedies occur, says nothing about the existence of gods or that we should believe in a certain way.
argumentum ad baculum: An argument based on an appeal to fear or a threat. (e.g., If you don’t believe in God, you’ll burn in hell)
argumentum ad ignorantiam: A misleading argument used in reliance on people’s ignorance.
argumentum ad populum: An argument aimed to sway popular support by appealing to sentimental weakness rather than facts and reasons.
bandwagon fallacy: concluding that an idea has merit simply because many people believe it or practice it. (e.g., Most people believe in a god; therefore, it must prove true.) Simply because many people may believe something says nothing about the fact of that something. For example many people during the Black plague believed that demons caused disease. The number of believers say nothing at all about the cause of disease.
begging the question (or assuming the answer): (e.g., We must encourage our youth to worship God to instill moral behavior.) But does religion and worship actually produce moral behavior?
circular reasoning: stating in one’s proposition that which one aims to prove. (e.g. God exists because the Bible says so; the Bible exists because God influenced it.)
composition fallacy: when the conclusion of an argument depends on an erroneous characteristic from parts of something to the whole or vice versa. (e.g., Humans have consciousness and human bodies and brains consist of atoms; therefore, atoms have consciousness. Or: a word processor program consists of many bytes; therefore a byte forms a fraction of a word processor.)
confirmation bias (similar to observational selection): This refers to a form of selective thinking that focuses on evidence that supports what believers already believe while ignoring evidence that refutes their beliefs. Confirmation bias plays a stronger role when people base their beliefs upon faith, tradition and prejudice. For example, if someone believes in the power of prayer, the believer will notice the few “answered” prayers while ignoring the majority of unanswered prayers (which would indicate that prayer has no more value than random chance at worst or a placebo effect, when applied to health effects, at best).
confusion of correlation and causation: (e.g., More men play chess than women, therefore, men make better chess players than women. Or: Children who watch violence on TV tend to act violently when they grow up.) But does television programming cause violence or do violence oriented children prefer to watch violent programs? Perhaps an entirely different reason creates violence not related to television at all. Stephen Jay Gould called the invalid assumption that correlation implies cause as “probably among the two or three most serious and common errors of human reasoning” (The Mismeasure of Man).
excluded middle (or false dichotomy): considering only the extremes. Many people use Aristotelian either/or logic tending to describe in terms of up/down, black/white, true/false, love/hate, etc. (e.g., You either like it or you don’t. He either stands guilty or not guilty.) Many times, a continuum occurs between the extremes that people fail to see. The universe also contains many “maybes.”
half truths (suppressed evidence): A statement usually intended to deceive that omits some of the facts necessary for an accurate description.
loaded questions: embodies an assumption that, if answered, indicates an implied agreement. (e.g., Have you stopped beating your wife yet?)
meaningless question: (e.g., “How high is up?” “Is everything possible?”) “Up” describes a direction, not a measurable entity. If everything proved possible, then the possibility exists for the impossible, a contradiction. Although everything may not prove possible, there may occur an infinite number of possibilities as well as an infinite number of impossibilities. Many meaningless questions include empty words such as “is,” “are,” “were,” “was,” “am,” “be,” or “been.”
misunderstanding the nature of statistics: (e.g., the majority of people in the United States die in hospitals, therefore, stay out of them.) “Statistics show that of those who contract the habit of eating, very few survive.” — Wallace Irwin
non sequitur: Latin for “It does not follow.” An inference or conclusion that does not follow from established premises or evidence. (e.g., there occured an increase of births during the full moon. Conclusion: full moons cause birth rates to rise.) But does a full moon actually cause more births, or did it occur for other reasons, perhaps from expected statistical variations?
no true Christian (no true Scotsman): an informal logical fallacy, an ad hoc attempt to retain an unreasoned assertion. When faced with an example, rather than denying it, this fallacy excludes the specific case without reference to any objective rule. Example: Many Christians in history have started wars. Reply: Well no true Christian would ever start a war.
observational selection (similar to confirmation bias): pointing out favorable circumstances while ignoring the unfavorable. Anyone who goes to Las Vegas gambling casinos will see people winning at the tables and slots. The casino managers make sure to install bells and whistles to announce the victors, while the losers never get mentioned. This may lead one to conclude that the chances of winning appear good while in actually just the reverse holds true.
post hoc, ergo propter hoc: Latin for “It happened after, so it was caused by.” Similar to a non sequitur, but time dependent. (e.g. She got sick after she visited China, so something in China caused her sickness.) Perhaps her sickness derived from something entirely independent from China.
proving non-existence: when an arguer cannot provide the evidence for his claims, he may challenge his opponent to prove it doesn’t exist (e.g., prove God doesn’t exist; prove UFO’s haven’t visited earth, etc.). Although one may prove non-existence in special limitations, such as showing that a box does not contain certain items, one cannot prove universal or absolute non-existence, or non-existence out of ignorance. One cannot prove something that does not exist. The proof of existence must come from those who make the claims.
red herring: when the arguer diverts the attention by changing the subject.
reification fallacy: when people treat an abstract belief or hypothetical construct as if it represented a concrete event or physical entity. Examples: IQ tests as an actual measure of intelligence; the concept of race (even though genetic attributes exist), from the chosen combination of attributes or the labeling of a group of people, come from abstract social constructs; Astrology; god(s); Jesus; Santa Claus, black race, white race, etc.
slippery slope: a change in procedure, law, or action, will result in adverse consequences. (e.g., If we allow doctor assisted suicide, then eventually the government will control how we die.) It does not necessarily follow that just because we make changes that a slippery slope will occur.
special pleading: the assertion of new or special matter to offset the opposing party’s allegations. A presentation of an argument that emphasizes only a favorable or single aspect of the question at issue. (e.g. How can God create so much suffering in the world? Answer: You have to understand that God moves in mysterious ways and we have no privilege to this knowledge. Or: Horoscopes work, but you have to understand the theory behind it.)
statistics of small numbers: similar to observational selection (e.g., My parents smoked all their lives and they never got cancer. Or: I don’t care what others say about Yugos, my Yugo has never had a problem.) Simply because someone can point to a few favorable numbers says nothing about the overall chances.
straw man: creating a false or made up scenario and then attacking it. (e.g., Evolutionists think that everything came about by random chance.) Most evolutionists think in terms of natural selection which may involve incidental elements, but does not depend entirely on random chance. Painting your opponent with false colors only deflects the purpose of the argument. (From the email that I get on NoBeliefs.com this appears as the most common fallacy of all.)
two wrongs make a right: trying to justify what we did by accusing someone else of doing the same. (e.g. how can you judge my actions when you do exactly the same thing?) The guilt of the accuser has no relevance to the discussion.
Use-mention error: confusing a word or a concept with something that supposedly exists. For example an essay on THE HISTORY OF GOD does not refer to an actual god, but rather the history of the concept of god in human culture. (To avoid confusion, people usually put the word or phrase in quotations.
Science attempts to apply some of the following criteria:
1) Skepticism of unsupported claims
2) Combination of an open mind with critical thinking
3) Attempts to repeat experimental results.
4) Requires testability
5) Seeks out falsifying data that would disprove a hypothesis
6) Uses descriptive language
7) Performs controlled experiments
8) Self-correcting
9) Relies on evidence and reason
10) Makes no claim for absolute or certain knowledge
11) Produces useful knowledge
Pseudoscience and religion relies on some of the following criteria:
1) Has a negative attitude to skepticism
2) Does not require critical thinking
3) Does not require experimental repeatability
4) Does not require tests
5) Does not accept falsifying data that would disprove a hypothesis
6) Uses vague language
7) Relies on anecdotal evidence
8) No self-correction
9) Relies on belief and faith
10) Makes absolute claims
11) Produces no useful knowledge
Some of this information derived in part from:
William D. Gray, “Thinking Critically About New Age Ideas”
Carl Sagan, “The Demon-Haunted World,” Random House, New York, 1995
The American Heritage Dictionary, Houghton Mifflin Company
Compiled by Jim Walker originated: 27 July 1997 additions made: 01 Dec. 2009